This traditional ‘cat-like’ mongoose,
and current resident of Madagascar, Cryptoprocta (Fig 1. 2), the fossa, >sometimes< nests basal to a series of cats, including Felis and Panthera (Fig 2), in the LRT (subset Fig 2). These arise from cat-like civets, like Genetta (Fig 3) and these from other traditional mongooses.
Earlier and traditionally civets nested far from cats despite their similarities.
Changes made far from these taxa currently move these taxa closer to – then further from – each other. So this nesting is not settled, but looks promising.
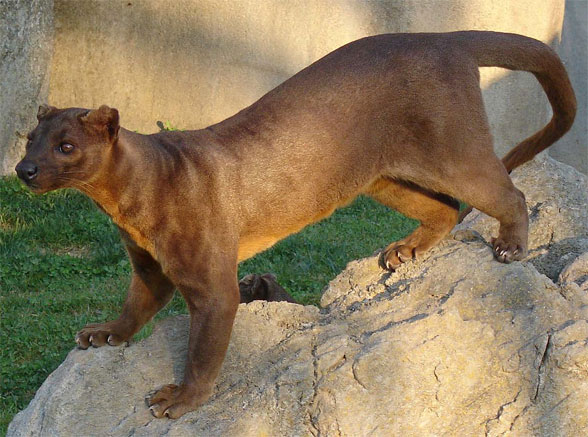

Figure 1. Cryptoprocta, a traditional mongoose, now nests at the base of cats in the LRT.
Seems obvious,
but Wikpedia reports, Cryptoprocta spelea, also known as the giant fossa, is an extinct species of carnivore from Madagascar in the family Eupleridae which is most closely related to the mongooses and includes all Malagasy carnivorans.
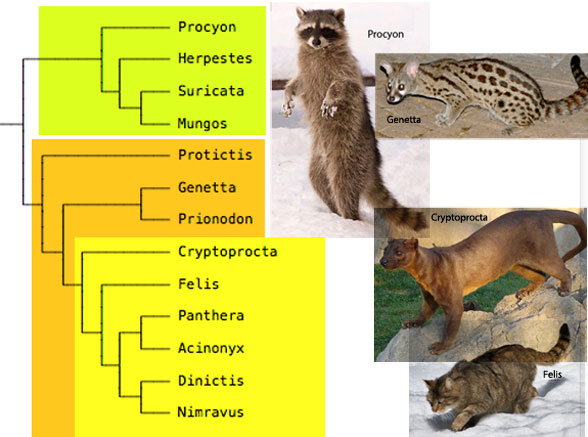
Figure 2. Subset of the LRT focusing on cats.
Madagascar split apart from Africa
155 mya and apart from India 88mya. So Cryptoprocta and its precursors, likely saw dinosaurs.
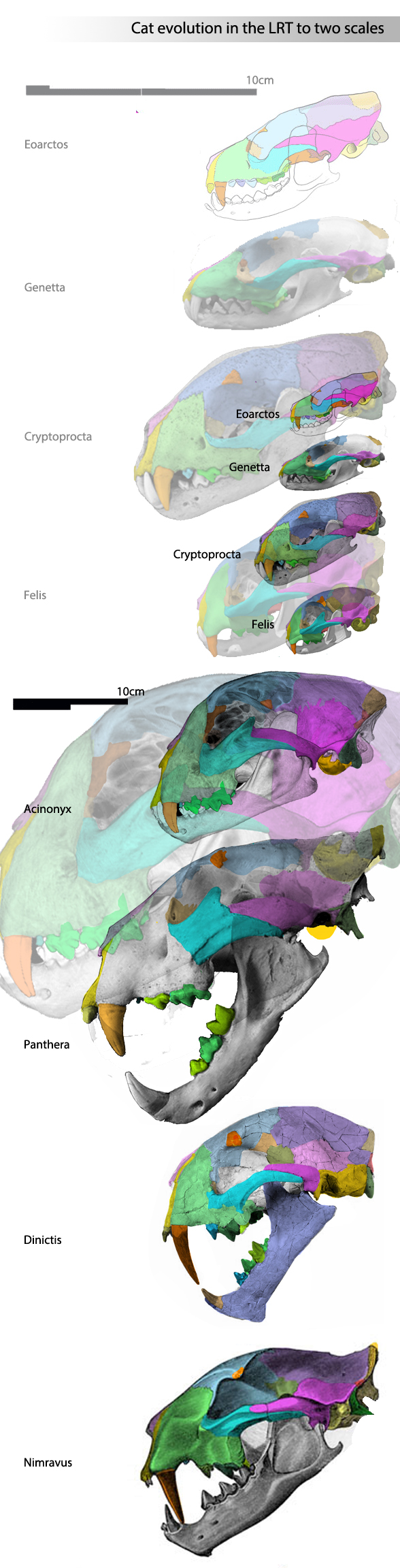
Figure 3. Cat skulls to two scales in phylogenetic order.
The LRT indicates that cats evolved from
civets and mongooses (including the basal mongoose, Procyon, the raccoon. It’s never a hard and fast break, but rather a fuzzy transition, like all evolutionary processes.
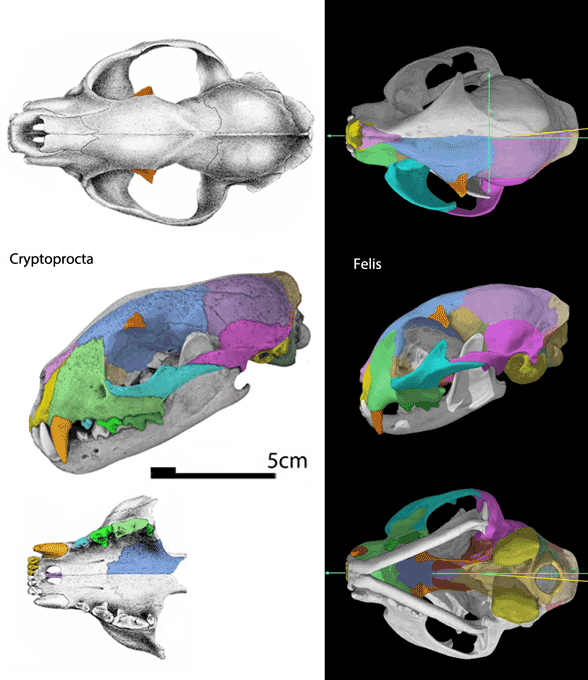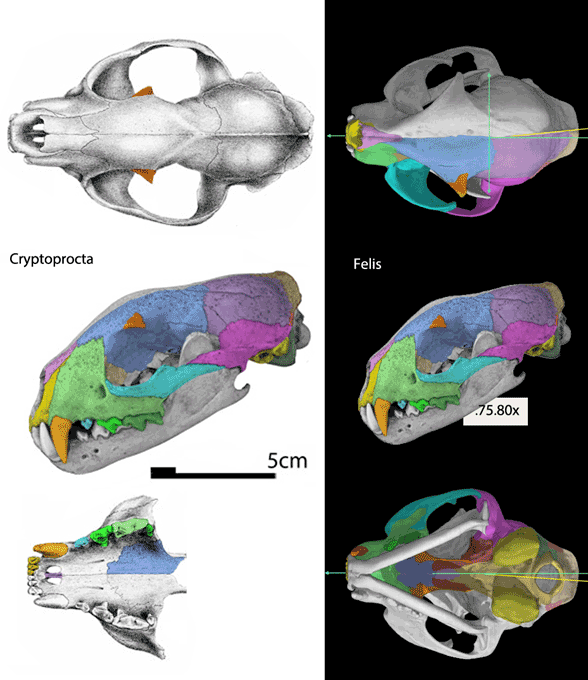
Figure 4. Cryptoprocta and Felis skulls to scale for comparison. Frame 2 reduces the Cryptoprocta skull to the size and shape of the Felis skull.
Worth remembering
Sabertooth ‘tigers’, like Smilodon, are not in this cat clade. Smilodon (Fig 5) arose from wolverines, like Gulo, and Arctodus, the short-faced ‘bear’, as recovered earlier here.
This also changes in the LRT as scores change in unrelated taxa.
Felis silvestris
(Schreber 1777) is the extant wildcat and house cat, here nesting betwween Cryptoprocta and Acinonyx, then Panthera. Note the flatter face and large orbits. These are neotonous traits carried into adulthood. Like other night hunters (bats, odontocetes, barn owls) the skull is torsioned to improve binaural abilities and the orbits are rotated anteriorly for better binocular vision.

Figure 5. Currently in the LRT, the ‘sabertooth tiger’ is more closely related to these dog-like and bear-like taxa than to cats.
Cryptoprocta ferox
(Bennett 1833) is the extant fossa, a cat-like mongoose from Madagascar. This isolation of this taxon on Madagascar demonstrates its antiquity because Madagascar split from Africa 135 mya.
I wish results were more settled here.
Even so, there is value in seeing new possibilities while shedding light on the high degree of convergence in the clade Carnivora. Every day there is something new to learn here.
This is an ongoing online experiment, constantly under modification.
References
Bennett ET 1833. Notice of a new genus of Viverridous Mammalia from Madagascar. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London. 1833: 46.
Schreber JCDv 1777. Die Säugetiere in Abbildungen nach der Natur mit Beschreibungen.
wiki/Cryptoprocta_spelea
wiki/Cryptoprocta
wiki/Cat
wiki/Felis – Wildcat
